• Production of goods in large quantities by processing raw material to form valuable product is called manufacturing.
• Manufacturing industries fall in the Secondary sector.
• For example paper from wood, sugar from sugarcane, etc.
Que.: Why this sector is important?
Ans.:
1. People employed in the secondary activities manufacture primary materials in to the finished goods.
2. Country's economic growth is measured by the development of manufacturing industries.
Que: "The Economic Strength of country is measured by the development of manufacturing industries". Support the statement with arguments.
( CBSE 2016 & 2017)
Ans.: (i) Manufacturing industries help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy.
(ii) Manufacturing industries also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
(iii) Industrial development reduces unemployment and poverty:
(iv) It also brings down regional disparities.
(v) Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings foreign exchange.
(vi) Prosperity of our country depends on transforming raw materials into furnished goods of higher value and diversifying our industries.
(vii) Industrial sector contributes 27% of GDP and manufacturing contributes 17% of GDP.
IMPORTANCE OF INDUSTRIES
• Help in modernising agriculture which forms the backbone of development.
• Reduces heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them job in secondary and tertiary sectors.
• Help in removal of unemployment and poverty.
• Aims at bringing down the regional differences by establishing industries in backward areas.
• Export of manufacturing goods expands trade and Commerce.
AGRICULTURE AND INDUSTRIES
• Agriculture and industry move hand in hand.
• Many Industries like sugar Exide at 17 depends on agriculture product. For example cotton is the raw material in the cotton textile mills.
• At the same time former many industrial like fertilizers irrigation pump, PVC pipe format tractors tool helps in increasing agricultural productivity.
Que.: "Agriculture and industries are not exclusive of each other." Support your answer by giving any three arguments. (CBSE 2011)
Ans.: Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other, rather they are interdependent on each other.
1. Agriculture provides the raw materials for most of the industries like textiles, rubber, sugar and industries offer the processing destination for the agricultural output.
2. If the agricultural sector is affected, its resultant effects can be seen in the industrial sector and vice versa. The agro - industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
3. They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers.
4. The competitiveness of the manufacturing industry has helped in increasing the productions abut have also made the production processes very efficient.
Que.: How should be the industries in globalised world?
Ans.: 1. Our Industries need to be more efficient and competitive.
2. Self - sufficiency alone is not enough.
3. Manufactured goods must be of good quality to comepetite international market.
CONTRIBUTION OF INDUSTRY TO NATIONAL ECONOMY
• During the last 20 years the share of manufacturing sector was stayed at 17% of GDP out of the total 27% for the industries.
• This is much lower in comparison to some East Asian economics, where it is about 25% to 35%.
• The desired growth rate over the next decade is 12% which has been around only 7% per annum is the last decade.
• To develop the sector of manufacturing industries, government has set up the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council ( NMCC).
Que.: Why has the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council been set up? (CBSE 2015)
Ans.: To develop the sector of manufacturing industries, government has set up the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council ( NMCC).
INDUSTRIAL LOCATION
The location of a factory is influenced by the government policies availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market facility.
Ideal Location of an Industry
1. Cost of obtaining raw material at site.
2. Cost of production at site.
3. Cost of distribution of production.
4. Decision to locate factory at site.
Que.: Describe the various physical and human factor responsible for the location of industries?
Ans.: (i) Physical Factors:
(a) Availability of raw materials—Ideal location should be near the sources of raw materials.
(b) Power resources—Power resources like coal and electricity must be available for the industry.
(c) Water and favourable climate.
(ii) Human Factors:
(a) Cheap and efficient labour.
(b) Capital and bank facilities.
(c) Good market.
(d) Transport facility.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INDUSTRIES AND CITIES
• Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand.
• After an industrial activity starts, organisations follows
• Sometimes, they are located in or near the city.
• Cities provide market and services such as banking transport labour etc. to industries.
• Many industries make use of advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economics.
Que.: "Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand" justify the statement by giving any three arguments. ( CBSE 2011)
Ans.: The given statement can be justified:-
(i) Industrialisation causes growth in available factory jobs. Thus, as employment rate increases it pulls people from various places and leads urbanisation.
(ii) People start moving towards cities for jobs and they gradually develop into urban centres. Sometimes industries are located in or near cities.
(iii) Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc to the industry.
Thus, it can be concluded that industrialisation and unbanisation go hand in hand.
INDUSTRY MARKET LINKAGE
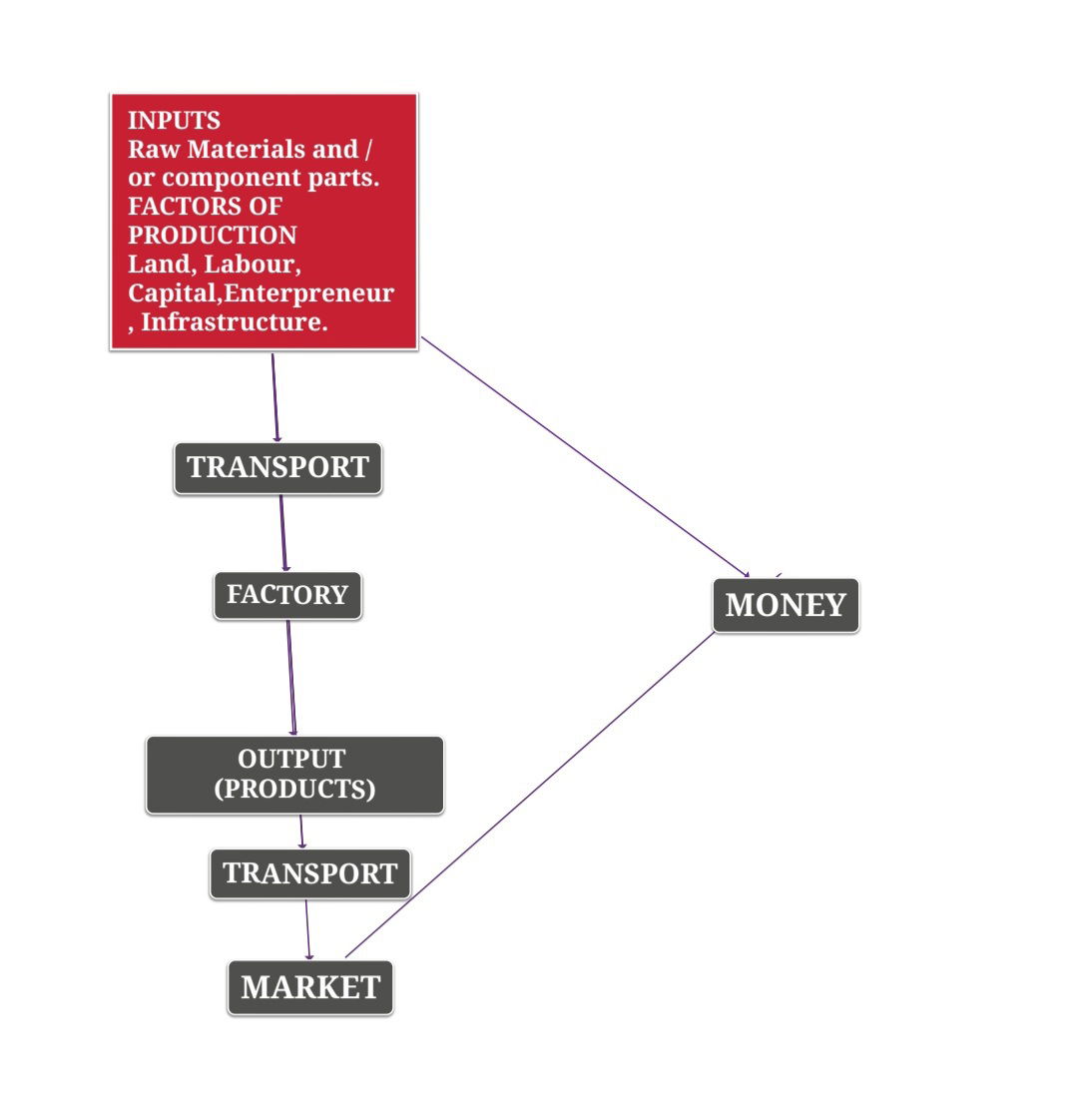 Fig.: Industry - Market linkage
Fig.: Industry - Market linkage
CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIES
1. On the basis of raw material used
• Agro based industries - cotton, wool silk ,textile, rubber, coffee etc.
• Mineral based industries - iron , steel ,cement aluminium machine tools etc.
2. On the basis of role played by them
• Basic or key industries:- Industries which supply their product as raw material to Other industries example iron steel etc.
• Consumer industries:- industries which produce goods for direct consumer use. For example sugar, paper,toothpaste etc.
3. On the basis of capital investment
• Small scale industry:-Industry with investment upto 1 crore.
• Large scale industry:- Industry with investment above 1 crore.
4. On the basis of ownership
• Public sector :- Owned and operated by the government Agencies. For example BHEL, SALE etc.
• Private sector :- Owned and operated by individual or group of individual. For example Bajaj Auto Limited, TISCO etc.
• Joint sector :- Jointly ran by the state and individuals. For example Oil India Limited.
• Cooperative sector:- owned and operated by the producer or supplier of raw material, worker or both. They share profit or losses proportionately. For example sugar industry in Maharashtra and coir industry in Kerala
5. On the basis of bulk and weight of raw material and finished good
• Heavy industries:- Large machine and heavy/ bulky raw material are used to produce product which are heavy or bulky, including capital goods like automobiles and construction machinery.
• Light industries:- Light Industries produced light utility goods. For example electrical and toy industries.
AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES
Textile industries
• It occupies a unique position in the Indian economy.
• Significantly contributes to industrial production (14%) Employment generation (35 million person) and foreign exchange earning (about 24.6%).
• Self reliant and complete in value chain ( that is from raw material to the highest value added product).
COTTON TEXTILE INDUSTRIES
• Ancient India :- Cotton textile were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques.
• 18th Century :- Power loom came into use.
• Colonial Period :- Suffered setback as they could not compete with the mill hand cloth from England.
• First textile mill was establish in Mumbai in 1854.
• Two world wars boosted the development of cotton textile industries in British India due to huge demand from England.
Que.: Name the most important agro based industry.
Ans.: Cotton Textile industry
LOCATION AND PROBLEM OF COTTON TEXTILE INDUSTRIES
Textile Industrial Regions
• Cotton textile industry is concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
• Availability of raw cotton, market, transport, labour, moist climate etc. contributed towards its localisation.
• Created employment opportunities to farmers, Cotton ball pluckers and workers.
• Support Other industries like chemical, packaging material, and engineering work.
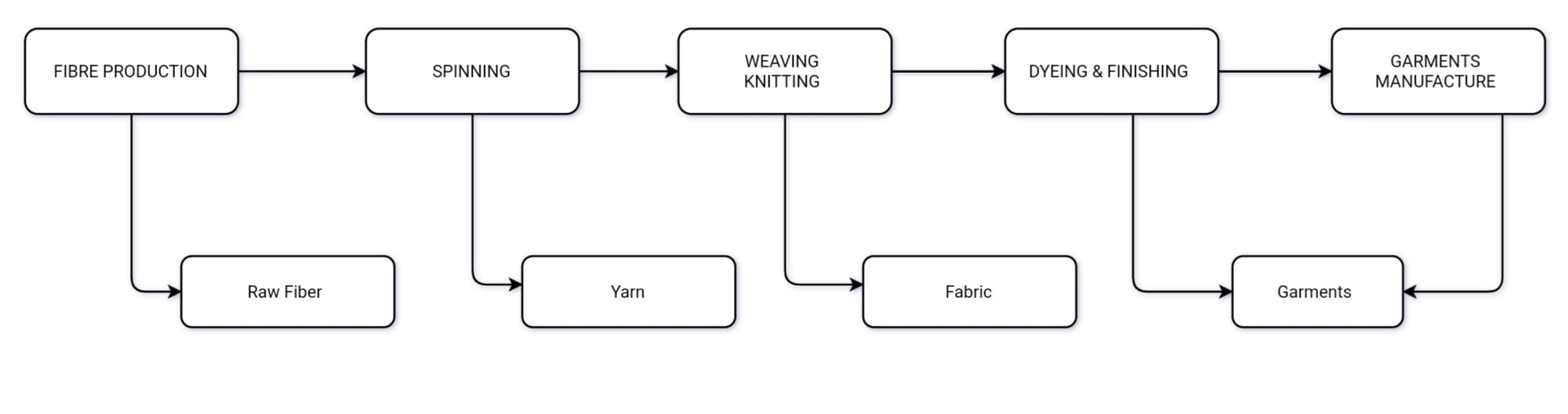
Fig.- Value addition in the textile industry
Cotton Textile Regions
• Spining continued to be centralised in Maharashtra Gujarat and Tamil nadu.
• Weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate the scope for cotton Silk, Zari and embroidery.
• Weaving is done by handloom, powerloom and in mills.
• Hand mandap khadi provides large scale employment.
Textile Trade
• India exports yarn to Japan.
• Importers of cotton Goods: USA, UK, Russia, France, East European countries etc.
• We have large share in the world trade of cotton yarn.
Drawbacks of textile industries
• Weaving knitting and Processing Units cannot use much of the high quality Yarn.
• Most of the production in this segment is fragmented into small units.
• Many of our spinner export cotton yarn and garment manufacturers import fabrics.
Problems of Cotton Textile Industries
• Power supply is erratic.
• Machinery need to be upgraded in weaving and processing sector.
• Low output of labour.
• Stuff competition with the synthetic fibre industry.
• There are significant increase in the production of good quality cotton but the need to import the same is still left.
JUTE TEXTILE
• India is a largest producer of raw jute and jute goods.
• Most of Jute mills are located along Hugli river in West Bengal due to favourable conditions.
• Jute is used in making rope, bags, carpets, artifacts etc.
• Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam and Tripura also have Jute mills.
• First Jute mill was set up in Rishra (Kolkata) in 1859.
• After partition in 1947 three fourth of jute producing area went to Bangladesh.
Why jute Industries mainly located in Hugli basin
• Raw jute is available for West Bengal and it is largest producer.
• Coal for energy is brought from nearby Rajganj coalfields.
• Hugli river provides water for washing and cleaning jutes.
• Warm and humid climate is very favourable for cultivation of jute.
• Kolkata is a metro city which provides capital and market along with cheap labours.
Pros and cons of jute production
• Tough competition from synthetic fibre industry.
• Stiff competition from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil, Egypt, Thailand and Philippines.
• Internal demand for jute packaging has increased due to the government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging.
• Main markets are USA, Canada, Saudi Arab,UK, Australia and Ghana.
• Growing Global concern from environmental friendly and biodegradable materials has once again opened opportunity for jute product.
Que.: Which state is leading producer of jute product in India? (CBSE 2015)
Ans.: West Bengal
SUGAR INDUSTRY
• India stands 2nd in the world in sugar production and 1st in the production of gur and Khandsari.
• Sugar Mills are located in UP, Bihar, Maharashtra, Tamil nadu etc.
• It is seasonal in nature and ideally suited for Cooperative sector.
• Nearly 60% mills are located in UP.
• In recent years there is a tendency for the Mills to concentration move in Southern and Western state specially in Maharashtra.
• Because sugarcane of these regions has a higher sucrose content and relatively colder climate is good for longer crushing season.
• Cooperative are successful in these states.
Major Challenges
• Seasonal nature of industry.
• Old and inefficient method of production.
• Transport delay in reaching sugarcane to factory.
• Needs to maximise the use of by product like baggage.
MINERAL BASED INDUSTRIES
IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRIES
• Iron and steel is a basic industry as heavy medium and light industry depend on it for machines and electrical goods.
• Also considered as heavy industries as raw material and finished goods as both heavy and bulky.
• Public sector industry.
• Concentrated close to the mineral rich area of Chota Nagpur Plateau region in West Bengal, Jarkhand, Odisha, Karnataka and Tamilnadu.
• India ranked 3rd among the world crude producer by producing 95.6 million tonnes in 2016.
• It is the largest producer of sponge iron.
• Per capita consumption of steel was 63 kilogram per annum (as per 2016).
• In the 1950s China and India produced almost the same quality of Steel.
• Today China is the largest producer and consumer of Steel in the world.
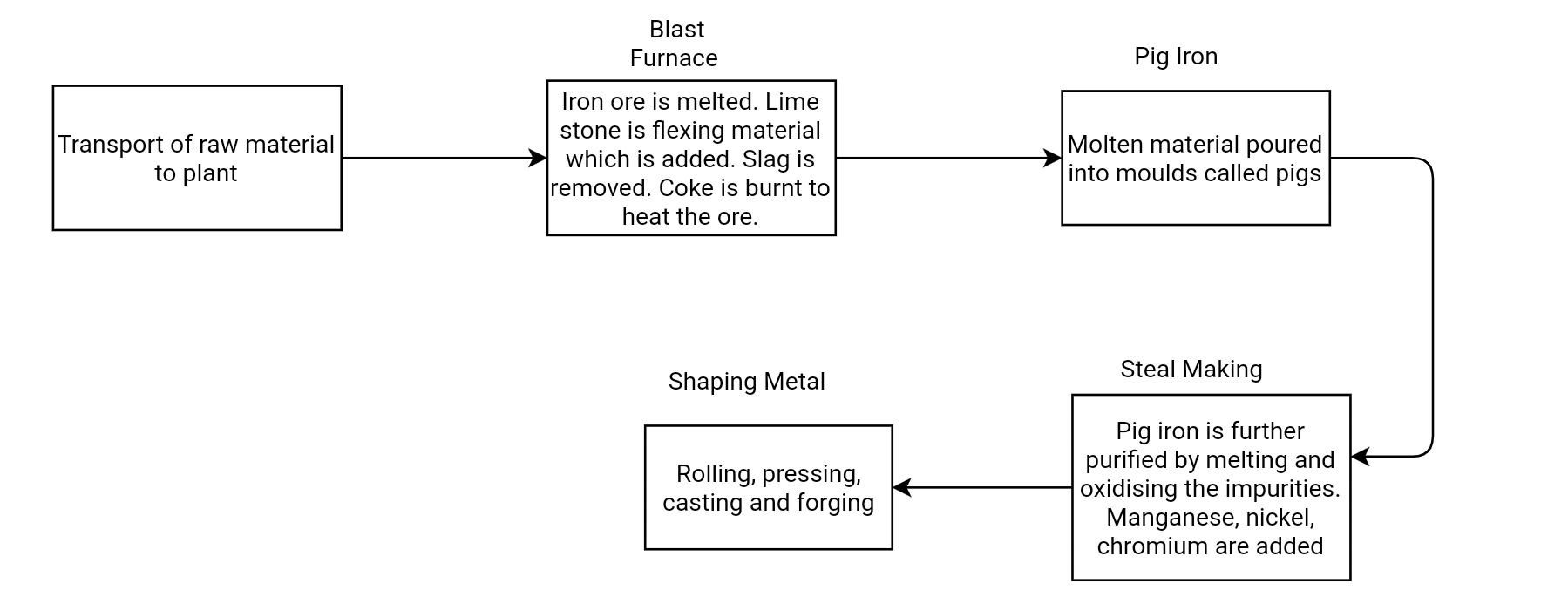
Fig.- Process of Manufacturing Steel
Factors responsible for the location of iron and steel industry in Chota Nagpur Plateau
• Close proximity to the areas where raw materials are found to reduce the transportation cost.
• Availability of cheap labours.
• Regular supply of water and power.
• Nearness to the market where finished product can be sold.
• Close to the sea port for export facility.
Challenges for Iron and Steel industries
• Limited availability and high cost of coking coal.
• Poor infrastructure.
• Irregular supply of energy.
• Low labour productivity.
Development of Steel in India
• Most of public sector undertaking market their Steel through Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL).
• We also import good quality of Steel from other countries, but overall production of it is sufficient to meet our domestic demand.
• Liberalization and foreign direct investment have boosted this industry.
ALUMINIUM SMELTING
• It is second most popular metallurgical industry of India.
• Raw materials used in balki dark reddish Rock known as a bauxite.
• It is light, resistant to corrosion, and a good conductor of heat and is malleable.
• It becomes stronger when mixed with other metals.
• It is used to manufacture aircraft, utensils and wires.
• Regular supply of electricity and raw material at maximum cost are two prime factor for its location.
• Major sources are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
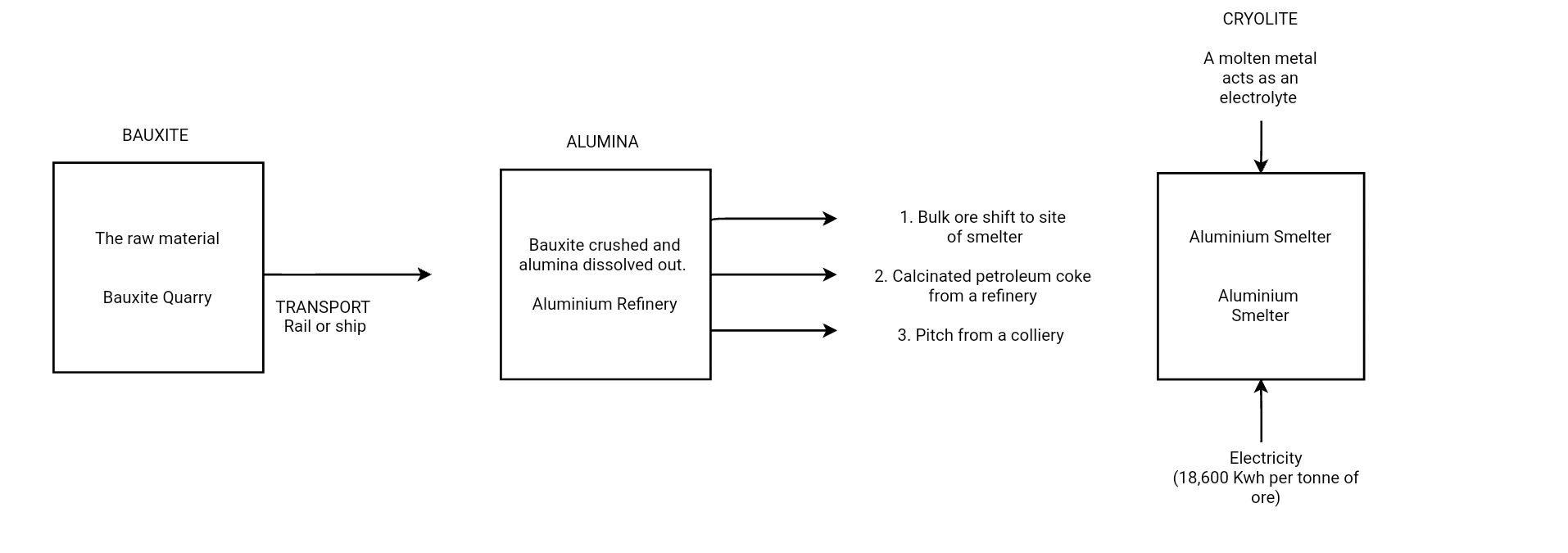
Fig.- Process of Manufacturing in Aluminium industry
CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
• Chemical industry is fast growing and diversifying industry in India.
• Compromises both large scale and small scale manufacturing units.
• Both organic and inorganic sector of the industry are rapidly growing.
• Organic Chemical:- include petrochemical which are used for manufacturing of synthetic fibre, synthetic rubber, plastics, dyestuff etc.
• Organic Chemicals Plant located near oil refineries or petrochemical plant.
• Inorganic Chemicals:- includes sulfuric acid, nitric acid, alkali soda ash, caustic soda etc.
• Chemical industry is its own largest consumer.
• Basic Chemicals were further process to obtain other chemicals for industrial applications, agriculture consumers etc.
FERTILIZER INDUSTRY
• Centred around the production of Nitrogenous fertilizers, Phosphatic fertilizers, Ammonium phosphate and Complex fertilizers.
• Complex fertilizer have a combination of Nitrogen(N) Phosphate(P) and Potash(K).
• Potash is entirely important because India does not have commercially viable potash.
• Green revolution expanded it to several other parts of country.
• Major producers :- Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Kerala contributes half of the countries produce.
• Other producers :-Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Bihar, etc.
CEMENT INDUSTRY
• Cement industry requires bolati raw materials like limestone, silica, aluminiua and gypsum.
• Coal, electric power, and Railway transportation are other requirements.
• Used for construction activity and for other commercial establishment.
• The first Cement Plant was setup in Chennai in 1904.
• After independence cement industries expanded in the country.
• There are many cement plants in Gujarat because of proximity to ports.
• Improvement in quality has found are readily available market in East Asia, Middle East, Africa and South Asia.
• Doing well in terms of production as well as export.
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY
• Automobiles provides vehicle for quick transport of goods services and passengers.
• Trucks, buses, cars, motor cycle, scooters, three wheelers, and multi utility vehicles are manufactured in India.
• Liberalization stimulated the demand for new and contemporary models in the market.
• Located around Gurugram, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur, Delhi and Bangalore.
Que.: Examine the impact of liberalisation on the automobile industry of India. (CBSE - 2012).
Ans.: 1. Multi utility vehicles have been introduced.
2. Becoming of new and contemporary models.
3. FDI in new technology.( FDI stands for Foreign Direct Investment).
4. Healthy grow of the market.
5. Liberalisation aligned the industry with Global development so industry has experienced a quantum jump.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) & ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY
• Cover products from transistor set to televisions, telephone, cell phones, Telephone Exchange, radar, computer and other equipment required by the the telecommunication and computer industry.
• Bengaluru has emerged as electronic capital of India.
• Other important centres for electronic goods are Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow and Coimbatore.
• Major Industries centres are Bengaluru, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad and Pune.
• It was a wide impact on Employment generation.
• Key success of IT industry in India in its continuous growth in both hardware and software.
Que.: What are software technology park? State any two points of significance of Information Technology industry in India. ( CBSE 2012)
Ans.:- Software Technology parks are a duster of Software Exports unit in which software technology companies develop and export computer software and other professional services.
Significance
1. Creation of a large number of jobs with more than 30% of women.
2. Large contribution to the export of India bringing in valuable foreign exchange.
3. The contribution growth in the hardware and software is the key of IT industry in India.
INDUSTRIAL POLLUTION AND ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION
• Industries have contributed significantly to India's economy growth and development.
• At the same time increase in the pollution cannot be over looked.
• Basically industries are responsible for four types of population that is air pollution, water pollution, thermal pollution and noise pollution.
Air Pollution
• Caused by the presence of high proportion of Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide in the air.
• Emitted by the chemical and paper factories, ,smelting plants and burning of fossil fuels in big and small factories.
• Causes respiratory problem.
• Toxic gas leaks at a time are very dangerous.
• For example :- Bhopal gas tragedy.
Water Pollution
• It is caused when organic and inorganic untreated Industrial waste are discharged into the river.
• Dyeing, petroleum, refineries and electroplanting industries are the main industries causing water pollution.
• They release dye, detergent, acid, metals,mercury, plastic etc into water.
• It threatens plant aquatic and human life.
Thermal pollution
• This occurs when hot water from factories and Thermal plant is drained into the river and pond, before colling.
• Waste from nuclear power plant, nuclear and weapon production facilities cause cancer birth defect and miscarriages.
• Dumping of waste such as glass, harmful chemical industrial effluent etc make the soil useless.
• Rainwater percolates carrying pollutant contaminate groundwater.
Noise Pollution
• Noise from Industrial and construction activities, machinery factory equipment etc. contribute to noise pollution.
• This type of pollution result in hear impairment, increased heart rate, Blood pressure, and physiological effects.
CONTROL OF ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION
How to Control?
• Minimising water use by reducing and recycling waste water in two or more successive stages.
• Rainwater harvesting to meet water requirement.
• Treating hot water and industrial waste before releasing them in river and ponds.
Three Phases of treatment of Industrial Effluents
• Primary treatment by mechanical mean. (that is screening grinding flocculation and sedimentation).
• Secondary treatment by biological processes (such as planting trees, rain water harvesting).
• Tertiary treatment by chemical physical and biological process. (like recycling of wastewater).
General Points to minimize Environmental Pollution
• Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industries needs to be regulated regularly.
• Generator and other machinery should be fitted with silencer to reduce their Sound.
• Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smokestacks to factories.
• Electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and internal separators can be used with smoke stacks.
• Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factory.
• Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
🖋Posted by
Surya Pratap Singh
